What is Multiple Pregnancy?
Multiple pregnancy happens when a woman carries more than one baby at the same time. This can mean twins, triplets, or even more. In recent years, multiple pregnancy has become more common. This is partly due to fertility treatments and older maternal age. Because multiple pregnancy can bring extra risks, it is important to know what to expect. Early care and regular check-ups help keep both mother and babies healthy.
Common Symptoms of Multiple Pregnancy
Many women wonder how to tell if they have a multiple pregnancy. While some symptoms are like those of a single pregnancy, others may feel stronger or appear earlier. For example, you may notice:
However, these signs alone do not confirm a multiple pregnancy. Only a doctor can make a clear diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the chance of having a multiple pregnancy. Some of these are natural, while others relate to medical treatments. For instance, you may be at higher risk if:
Still, sometimes multiple pregnancy happens without any clear reason.
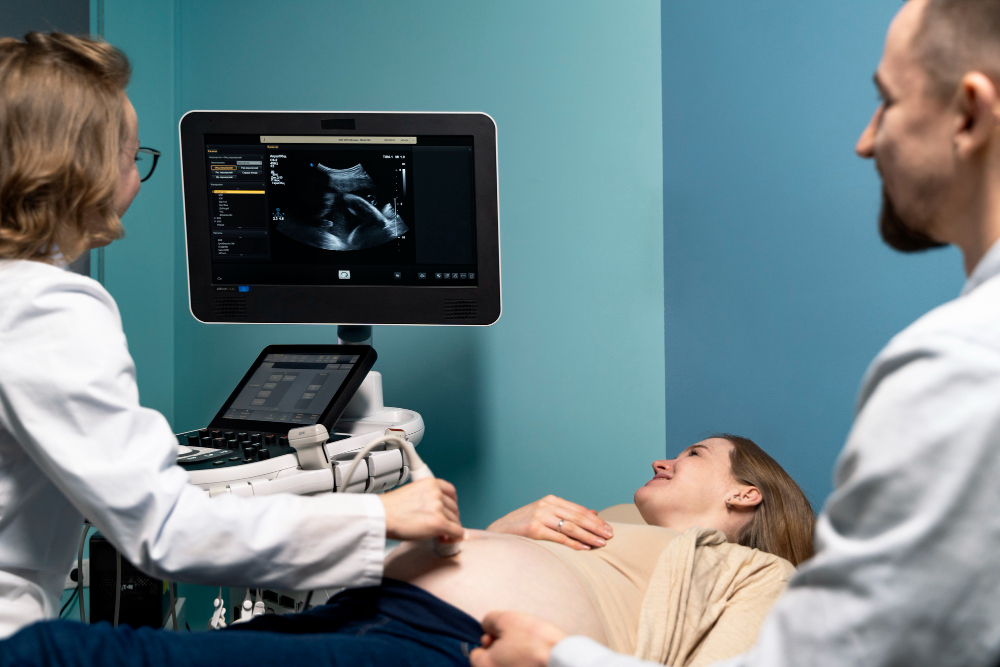
How Multiple Pregnancy is Diagnosed
Doctors use several ways to diagnose multiple pregnancy. Early in pregnancy, your doctor may notice a larger uterus or hear more than one heartbeat. However, the most reliable way is through an ultrasound scan. This test uses sound waves to create pictures of the babies. Usually, an ultrasound can confirm multiple pregnancy as early as the first trimester. Blood tests that show high levels of certain hormones may also suggest more than one baby, but they are not enough on their own.
Potential Risks and Complications
Multiple pregnancy can bring extra risks for both mother and babies. Some of the most common risks include:
Because of these risks, regular prenatal care is very important. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) both stress the need for close monitoring during multiple pregnancy.
Care and Management Tips
Proper care can help improve outcomes in multiple pregnancy. Here are some helpful tips:
In some cases, your doctor may suggest extra tests or more frequent check-ups. This helps catch any problems early.
Prevention and When to Seek Help
While you cannot always prevent multiple pregnancy, you can lower risks by:
However, if you have a multiple pregnancy, it is vital to know when to seek help. Contact your healthcare provider right away if you notice:
Early action can protect both you and your babies.
For personalized advice on multiple pregnancies, consult Dr. Rupa Pandra. Regular prenatal care and early support can make a significant difference for you and your growing family.